The Legendary Transformation: 3D Printing in Future Manufacturing
Unveiling the Innovation of 3D Printing
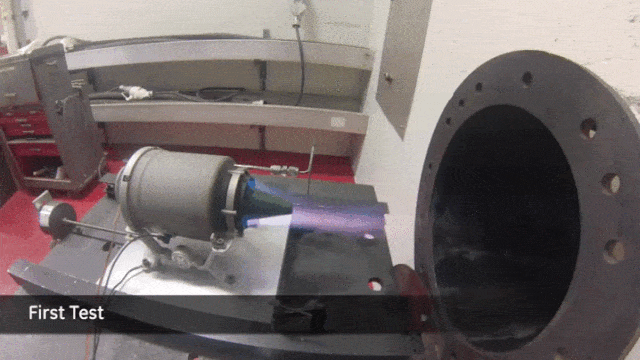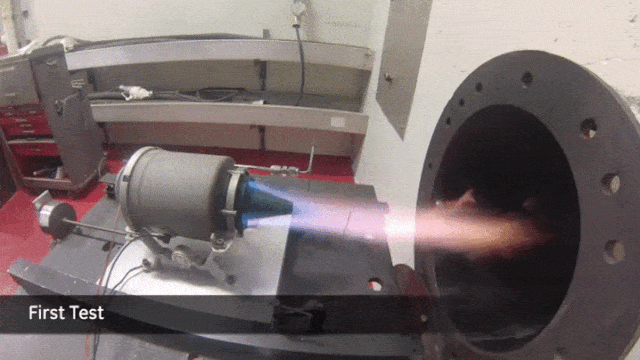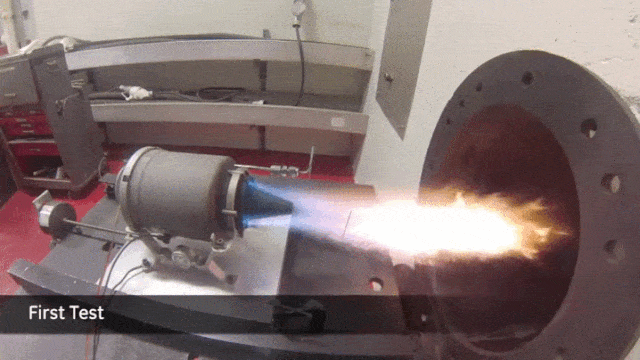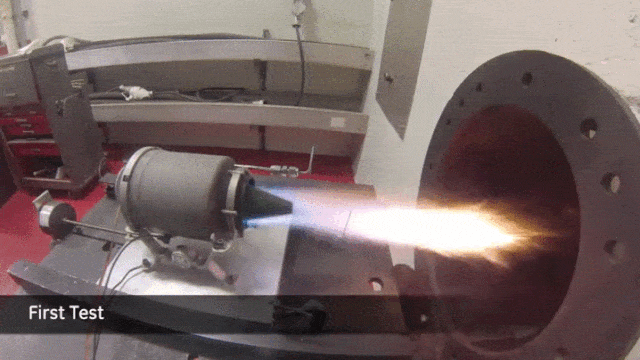
Another area that promises groundbreaking possibilities is bioprinting. Spearheaded by companies like Organovo, this emerging field harnesses cutting-edge organic printing technologies to fabricate intricate biological structures.
Beyond its current capabilities, the potential applications of bioprinting in the medical field over the next decade are staggering. Imagine a future where custom-designed organs and tissues can be printed on demand, offering life-saving solutions for patients in need of transplants.
Bioprinting holds the potential to transform drug testing and research, providing more accurate models of human physiology for pharmaceutical development.
As this technology continues to mature, it has the power to revolutionize not just medical treatments but the entire healthcare industry, ushering in a new era of personalized medicine and improved patient outcomes.
Speed and Efficiency
The perception of 3D printing as a slow process is rapidly becoming antiquated as advancements in technology propel the industry forward at an unprecedented pace.
A prime example of this acceleration is HP's Multi Jet Fusion technology, which has revolutionized the landscape of additive manufacturing. Unlike conventional 3D printing methods, Multi Jet Fusion boasts remarkable speed and efficiency, allowing for rapid prototyping and even scaling up to mass production levels.
This breakthrough technology operates by fusing layers of material together with remarkable precision and speed, significantly reducing production times compared to traditional methods. By harnessing the power of Multi Jet Fusion, manufacturers can iterate designs more quickly, accelerate product development cycles, and respond rapidly to changing market demands.
The enhanced speed and efficiency of this technology have opened doors to new possibilities in customization and on-demand manufacturing, enabling businesses to offer tailored products to consumers with unprecedented agility.
As emerging technologies continue to push the boundaries of what's achievable in 3D printing, the era of slow, labor-intensive additive manufacturing is swiftly giving way to a new era of speed, efficiency, and limitless innovation.
Economic Renaissance: Cost Effectiveness in 3D Printing
The Green Chronicle: 3D Printing and Sustainability
Waste Reduction: A Sustainable Saga
The narrative of waste reduction through 3D printing unfolds as a compelling saga of sustainability. One notable protagonist in this story is SpaceX, where the utilization of 3D printing has transformed the manufacturing landscape, particularly in the realm of rocket production. By embracing additive manufacturing techniques, SpaceX has minimized waste generation significantly, a stark departure from the inefficiencies inherent in traditional subtractive manufacturing processes. The precision afforded by 3D printing technology allows intricate rocket parts to be fabricated with remarkable accuracy, ensuring that material usage is optimized to the fullest extent. Consequently, not only are material costs reduced, but the environmental impact of manufacturing is also substantially mitigated. This shift towards a more sustainable production paradigm underscores the transformative potential of 3D printing in addressing the pressing challenges of resource conservation and waste management.
Moreover, beyond the aerospace industry, the ripple effects of waste reduction through 3D printing reverberate across various sectors. From automotive to healthcare, companies are leveraging additive manufacturing to minimize material wastage and embrace more eco-friendly production practices. By harnessing the precision and efficiency of 3D printing, manufacturers can achieve unprecedented levels of resource optimization, paving the way for a more sustainable future. As sustainability becomes an increasingly central concern in global discourse, the role of 3D printing as a catalyst for waste reduction emerges as a beacon of hope, offering tangible solutions to the environmental challenges of our time.
